CUFIX: Non-bonded Fix (NBFIX) parameters for the CHARMM and AMBER force fields
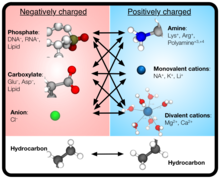
Over the past decades, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of biomolecules have become a mainstream biophysics technique. As the length and time scales amenable to the MD method increase, shortcomings of the empirical force fields—which were developed and validated using relatively short simulations of small molecules—become apparent. One common artifact is artificial aggregation of water-soluble biomolecules, which has been observed in a variety of systems, including electrolyte solutions, intrinsically disordered proteins, lipid bilayer membranes and DNA arrays. Here, we report a systematic refinement of Lennard-Jones parameters (CUFIX) describing amine-carboxyate, amine-phosphate, and aliphatic carbon-carbon interactions, which brings the results of MD simulations of proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids in remarkable agreement with experiments. To refine the amine-carboxylate and aliphatic carbon-carbon interactions, we matched the simulated osmotic pressure of amino acid solutions to the experimental data. Similarly, we refined the amine-phosphate interaction by matching the simulated and experimental osmotic pressure of a DNA array. We demonstrate the utility of our CUFIX corrections through simulations of lysine-mediated DNA—DNA forces, lipid-bilayer membranes and folded proteins. As our refinement neither affects the existing parameterization of bonded interaction nor does it alter the solvation free energies, it improves realism of an MD simulation without introducing any new artifacts.
How to use CUFIX (contact Jejoong Yoo jejoong@gmail.com):
-
AMBER ff99/ff14 variants in the Gromacs format:
-
> Option 1: If you want to use a complete package that was used for our publications, download one of the followings. Make sure our CUFIX corrections are optimized with the TIP3P water model (use tip3p.itp).
-
> Option 2: If you want to integrate CUFIX to your version of AMBER ff99/ff14 variants, follow these steps.
-
>> Download ff99sb-ildn-phi-bsc0-cufix package.
-
>> Copy the following files in the downloaded package to your gromacs-format ff99 folder: cufix.itp, mg-sol6.itp mg-sol6.pdb ca-sol7.itp ca-sol7.pdb.
-
>> Replace atom types of O1P and O2P atoms (O2) with ON2 for all nucleotides in dna.rtp and rna.rtp. ON2 atom type is defined in cufix.itp.
-
>> Add #include "cufix.itp" to forcefield.itp between #include "ffnonbonded.itp" and #include "ffbonded.it".
-
>> Delete the following ions from ffnonbonded.itp: Li, Na, K, Cl, MG, Rb, Cs, F, Br, I. CUFIX uses new ion parameters by the Cheatham group.
-
>> You're ready to go! Make sure that CUFIX is optimized with tip3p.itp.
-
-
-
AMBER ff99/ff14 variants in AMBER format
-
> Download cufix.tar and untar in the amber16/dat/leap directory.
-
> For DNA and RNA, we prepared leaprc.DNA.bsc1.cufix and leaprc.RNA.OL3.cufix. In these files, we introduce ON2 atom type for the phosphate oxygen atoms to differentiate them from the carboxylate atom type O2.
> frcmod.ff99cufix file will work with any ff99 and ff14 variant protein force field in combination with leaprc.water.tip3p.
-
For example, do the followings in the leap command:
-
source <A FF99 PROTEIN FORCE FIELD CMD FILE>
source leaprc.water.tip3p
cufix = loadamberparams frcmod.ff99cufix
-
-
-
CHARMM 36/27/22 force fields
-
> Download CHARMM36/27/22 force fields: stream file for NAMD packages
-
> Replace the standard toppar_water_ions.str with the downloaded file.
-
> Our CUFIX corrections are optimized for CHARMM36-version ion parameters (LIT, SOD, K, MG, CAL and CL) with CHARMM-format TIP3P water model.
-
> For magnesium and calcium ions, we use hexa- or hepta-hydrated forms, respectively. The downloaded file contains RESI definitions for these Mg/Ca-water complexes, but additional bonds (extrabonds) are required between Mg/Ca and water oxygen atoms. Please refer to our DNA origami tutorial to learn how to use it.
-
- Anton
-
>Just use it the same way as the other force fields at $VIPARR3_FFDIR.
-