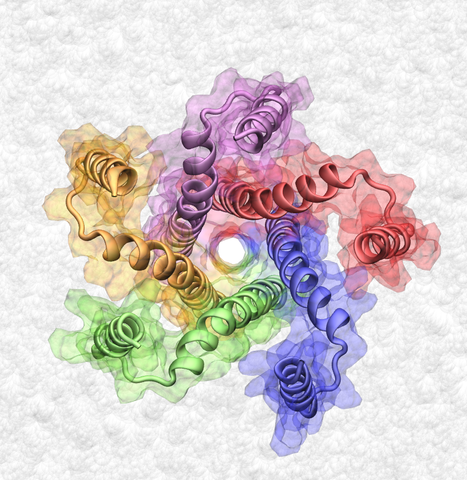
A 52-residue membrane protein, phospholamban (PLN) is an inhibitor of an adenosine-5'-triphosphate-driven calcium pump, the Ca2+-ATPase. Although the inhibition of Ca2+-ATPase involves PLN monomers, in a lipid bilayer membrane, PLN monomers form stable pentamers of unknown biological function. The recent NMR structure of a PLN pentamer depicts cytoplasmic helices extending normal to the bilayer in what is known as the bellflower conformation. The structure shows transmembrane helices forming a hydrophobic pore 4 Å in diameter, which is reminiscent of earlier reports of possible ion conductance through PLN pentamers. However, recent FRET measurements suggested an alternative structure for the PLN pentamer, known as the pinwheel model, which features a narrower transmembrane pore and cytoplasmic helices that lie against the bilayer. Here, we report on structural dynamics and conductance properties of the PLN pentamers from all-atom (AA) and coarse-grained (CG) molecular dynamics simulations. Our AA simulations of the bellflower model demonstrate that in a lipid bilayer membrane or a detergent micelle, the cytoplasmic helices undergo large structural fluctuations, whereas the transmembrane pore shrinks and becomes asymmetric. Similar asymmetry of the transmembrane region was observed in the AA simulations of the pinwheel model; the cytoplasmic helices remained in contact with the bilayer. Using the CG approach, structural dynamics of both models were investigated on a microsecond timescale. The cytoplasmic helices of the CG bellflower model were observed to fall against the bilayer, whereas in the CG pinwheel model the conformation of the cytoplasmic helices remained stable. Using steered molecular dynamics simulations, we investigated the feasibility of ion conductance through the pore of the bellflower model. The resulting approximate potentials of mean force indicate that the PLN pentamer is unlikely to function as an ion channel.